Home > African Marke > Zambia
Time: Jun 17, 2016
AIDS Epidemic and Response
AIDS epidemic in the country
Number of people living with HIV | 1,200,000 [1,100,000 - 1,200,000] |
Adults aged 15 to 49 prevalence rate | 12.4% [11.7% - 13.1%] |
Adults aged 15 and up living with HIV | 1,000,000 [980,000 - 1,100,000] |
Women aged 15 and up living with HIV | 540,000 [510,000 - 580,000] |
Children aged 0 to 14 living with HIV | 100,000 [98,000 - 110,000] |
Deaths due to AIDS | 19,000 [15,000 - 24,000] |
Orphans due to AIDS aged 0 to 17 | 380,000 [290,000 - 680,000] |
Source: HIV and AIDS estimates (2014)[1] from UNAIDS Data
General description: Zambia has a mature, generalized epidemic in which HIV transmission primarily occurs heterosexually. In the latest 2013-14 DHS, HIV prevalence in adults aged 15-49 years was estimated at 13.3%. Spectrum estimates of the HIV prevalence in adults aged 15-49 years suggest that the Zambian HIV epidemic has been fairly stable over the last 15 years with a very modest decline after the initial peak prevalence. The following figures illustrate the trends in prevalence of HIV among women and men aged 15-49.
National AIDS response
Testing: the proportion and number of people tested and counselled for HIV and received their results increased significantly from 2,066,216 in 2013 to 2,453,242 in 2014. This figure was below the target of 2,951,793.
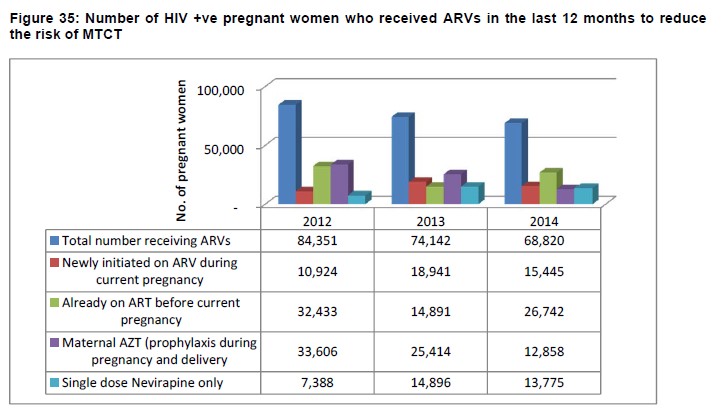
eMTCT: the percentage of HIV-positive pregnant women receiving ARVs was 93.72%, 96.65% and 91.26% in 2012, 2013 and 2014 respectively.
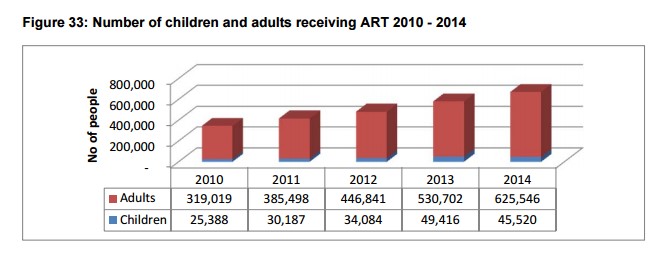
ART: The ART programme continues to show impressive performance. In 2014, a total of 671,066 adults and children (267,092 male and 403,974 female) were receiving antiretroviral. Of these, 108,334 were newly initiated during the year. 625,546 were adults 15 years old and above, which exceeded the target of 569,567.
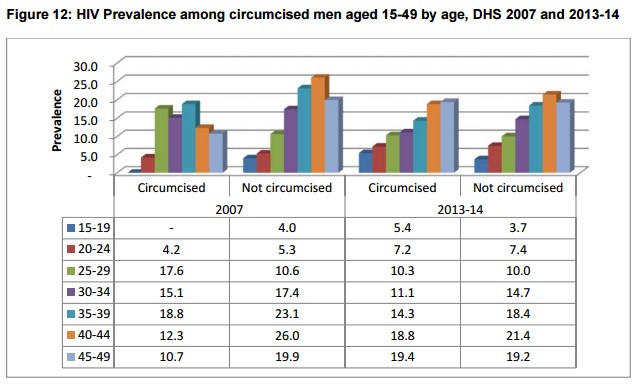
Male circumcision: HIV prevalence is slightly lower among men who are circumcised (10.1%) than among uncircumcised (11.7%) men. This pattern is more pronounced between urban and rural residence. The pattern is observed across most subgroups, except among men without education, and men from Southern and Eastern provinces, where circumcised men are more likely to be HIV positive than uncircumcised men.
Challenges and actions
1) Treatment: inadequate HIV testing facilities; limited numbers of ART centres in rural areas; the limited implementation of the task shifting of ART initiatives; low stock levels of ARV drugs experienced by majority of health centres in Zambia; services of Adolescents Living with HIV/AIDS (ALHIV) not meeting the needs of adolescents in most areas of the country; inadequate tracking system of PLHIV on treatment in certain areas; loss to follow-up;
2) Prevention: inadequate human resources and a shortage of trained staff in some of the departments and units of the health delivery system.
[1] http://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/zambia/